For anyone in London and at a loose end next Monday, 1 November, there’s an event on at the Royal Institution from 7 pm to 8.30 pm: Nanotechnology: can something so tiny promise something so big?. It’s a debate about nanotechnology and its potential, chaired by the science writer Philip Ball, and featuring myself, Ray Oliver, an industrial nanotechnologist and one of the authors of the recent Royal Society report, and James Wilsdon, from the thinktank Demos, whose recent pamphlet about ways to engage the public about new technologies such as nanotechnology, See-through Science, I wrote about below. It should be an interesting evening.
Category: General
A new laboratory for semiconductor nanotechnology at Sheffield
A suite of refurbished laboratories in my department (Physics and Astronomy, University of Sheffield) was formally opened yesterday by Dame Julia Higgins, chair of EPSRC and Vice President of the Royal Society. The labs were refurbished with money from the Wolfson Foundation and the Royal Society and now house Maurice Skolnick’s work in semiconductor nanotechnology, as well as my own group’s labs. We marked the occasion with a set of scientific seminars.
It’s always interesting to get an update on what one’s colleagues are up to, and Maurice’s talk had some stunning examples of recent progress in semiconductor nanotechnology. I’ll show just one example.
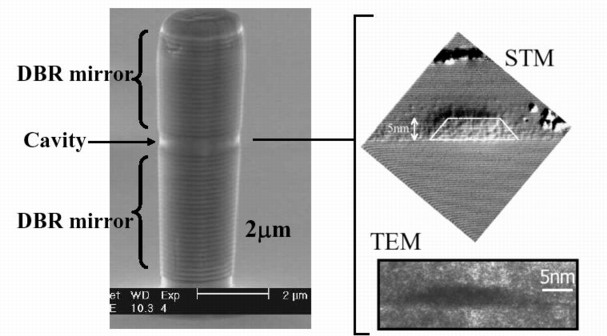
The picture shows (left) a very small diameter photonic micropillar – one can make out a central enclosure, the cavity, sandwiched between two distributed Bragg reflectors (DBRs). These are multilayers of different semiconductors which behave as near-perfect mirrors for light; photons generated inside the cavity are essentially trapped by the mirrors and the edge of the pillar.
Simply to make these intricately structured micropillars is enough of an achievement (these were made at Sheffield by A Tahraoui and P W Fry). But within the cavity there is a further level of control. The pictures on the right show individual quantum dots, grown by self-assembly. These are incorporated within the cavity of the structure on the left (the transmission electron micrograph, labelled TEM, comes from Hopkinson and Cullis at Sheffield, the scanning tunelling micrograph, labelled STM, from Skolnick’s collaborator P.M. Koenraad at Eindhoven). The resulting structure simultaneously exploits the quantum effects that occur when electrons are confined within the quantum dots, with the optical confinement effects that occur when photons are trapped within the cavity. This allows simultaneous control both of the energies of electronic states in the quantum dot and of the way transitions between electronic states are coupled to the emission of light.
Quantum dots of this kind are already used to make solid state lasers for use in optical communications. What is really exciting Maurice and his colleagues, though, is the possibility that this kind of structure might be used as the basis for a quantum computer. Quantum computers, if one could get them to work, offer the possibility of massively parallel computing of a power unparalleled with our current CMOS technologies. The problem is that one has to keep quantum states isolated from the environment enough to work their quantum magic, but one still has to retain the ability to interact with the states enough to provide some kind of input and output to the computations. This kind of structure, with its very close control both of the states themselves, and, via the photonic control, of their interactions with the outside world, may just possibly do the trick.
Then worms ‘ll come and eat thee oop
I had a late night in the prosperous, liberal, Yorkshire town of Ilkley last night, doing a talk and question and answer session on nanotechnology at the local Cafe Philosophique. An engaged and eclectic audience kept the discussion going well past the scheduled finish time. Two points particularly struck me. One recurring question was whether it was ever realistic to imagine that we can relinquish technological developments with negative consequences – “if it can be done, it will be done” was the comment made more than once. I really don’t like this conclusion, but I’m struggling to find convincing arguments against it. A more positive comment concerned the idea of regulation; we are used to thinking of this idea entirely in terms of narrow prohibitions – don’t release these nanoparticles into the environment, for example. But we need to work out how to make regulation a positive force that steers the technology in a desirable direction, rather than simply trying to sit on it.
(Non British readers may need to know that the headline is a line from a rather odd and morbid folk-song called “On Ilkley Moor baht hat”, sung mostly by drunken Yorkshiremen.)
What is this thing called nanotechnology? Part 2. Nanoscience versus Nanotechnology
In the first part of my attempt to define nanotechnology terms, I discussed definitions of the nanoscale. Now I come to the important and underappreciated distinction between nanoscience and nanotechnology.
Nanoscience describes the convergence of physics, chemistry, materials science and biology to deal with the manipulation and characterisation of matter on the nanoscale.
Many subfields of these disciplines have been dealing with nanoscale phenomena for many years. A very non-exhaustive list of relevant sub-fields, with examples of topics in nanoscience, would include:
The distinguishing feature of nanoscience is that increasingly we find methods and techniques from more than one of these existing subfields combined in novel ways.
Nanotechnology is an engineering discipline which combines methods from nanoscience with the disciplines of economics and the market to create usable and economically viable products.
Nanoscience and nanotechnology need to be distinguished. Without nanoscience, nanotechnology will not be possible. On the other hand, if you invest money in a nanoscience venture under the impression that it is nanotechnology, you are sure to be disappointed.
In the next installment, I’ll discuss the various kinds of nanotechnology, from incremental technologies such as shampoos and textile treatments to the more radical visions.
Training the nanotechnologists of the future
It’s that time of year when academic corridors are brightened by the influx of students, new and returning. I’m particularly pleased to see here at Sheffield the new intake for the Masters course in Nanoscale Science and Technology that we run jointly with the University of Leeds.
We’ve got 29 students starting this year; it’s the fourth year that the course has been running and over that time we’ve seen a steady growth in demand. I hope that reflects an appreciation of our approach to teaching the subject.
My view is that to work effectively in nanotechnology you need two things, First comes the in depth knowledge and problem-solving ability you get from studying a traditional discpline, whether that’s a pure science, like physics and chemistry, or an applied science, like materials science, chemical engineering or electrical engineering. But then you need to learn the languages of many other disciplines, because no physicist or chemist, no matter how talented at their own subject, will be able to make much of a contribution in this area unless they are able to collaborate effectively with people with very different sets of skills. That’s why to teach our course we’ve assembled a team from many different departments and backgrounds; physicists, chemists, materials scientists, electrical engineers and molecular biologists are all represented.
Of course, the nature of nanotechnology is such that there’s no universally accepted curriculum, no huge textbook of the kind that beginning physicists and chemists are used to. The speed of development of the subject is such that we’ve got to make much more use of the primary research literature than one would for, say, a Masters course in physics. And because nanotechnology should be about practise and commercialisation as well as theory we also refer to the patent literature, something that’s, I think, pretty uncommon in academia.
In terms of choice of subjects, we’re trying to find a balance between the hard nanotechnology of lithography and molecular beam epitaxy and the soft nanotechnology of self-assembly and bionanotechnology. The book of the course, “Nanoscale Science and Technology”, edited by my colleagues Rob Kelsall, Ian Hamley and Mark Geoghegan, will be published in January next year.
What is this thing called nanotechnology? Part 1. The Nano-scale.
Nanotechnology, of course, isn’t a single thing at all. That’s why debates about the subject often descend into mutual incomprehension, as different people use the same word to different things, whether it’s business types talking about fabric treatments, scientists talking about new microscopes, or posthumanists and futurists talking about universal assemblers. I’ve attempted to break the term up a little and separate out the different meanings of the word. I’ll soon put these nanotechology definitions on my website, but I’m going to try out the draft definitions here first. First, the all-important issue of scale.
Nanotechnologies get their name from a unit of length, the nanometer. A nanometer is one billionth of a metre, but let’s try to put this in context. We could call our everyday world the macroscale. This is the world in which we can manipulate things with our bare hands, and in rough terms it covers about a factor of a thousand. The biggest things I can move about are about half a meter big (if they’re not too dense), and my clumsy fingers can’t do very much with things smaller than half a millimeter.
We’ve long had the tools to extend the range of human abilities to manipulate matter on smaller scales than this. Most important is the light microscope, which has opened up a new realm of matter – the microscale. Like the macroscale, this also embraces roughly another factor of a thousand in length scales. At the upper end, objects half a millimeter or so in size provide the link with the macroscale; still visible to the naked eye, handling them becomes much more convenient with the help of a simple microscope or even a magnifying glass. At the lower end, the wavelength of light itself, around half a micrometer, gives a lower limit on the size of objects which can be discriminated even with the most sophisticated laboratory light microscope.
Below the microscale is the nanoscale. If we take as the upper limit of the nanoscale the half-micron or so that represents the smallest object that can be resolved in a light microscope, then another factor of one thousand takes us to half a nanometer. This is a very natural lower limit for the nanoscale, because it is a typical size for a small molecule. The nanoscale domain, then, in which nanotechnology operates, is one in which individual molecules are the building blocks of useful structures and devices.
These definitions are by the nature arbitrary, and it’s not worth spending a lot of time debating precise limits on length scales. Some definitions – the US National Nanotechnology Initiative provides one example – uses a smaller upper limit of 100 nm. There isn’t really any fundamental reason for choosing this number over any other one, except that this definition carries the authority of President Clinton, who of course is famous for the precision of his use of language. Some other definitions attempt to attach some more precise physical significance to this upper length limit on nanotechnology, by appealing to some length at which finite size effects, usually of quantum origin, become important. This is superficially appealing but unattractive on closer examination, because the relevant length-scale on which these finite size effects become important differs substantially according to the phenomenon being looked at. And this line of reasoning leads to an absurd, but commonly held view, that the nanoscale is simply the length-scale on which quantum effects become important. This is a very unhelpful definition when one thinks about it for longer than a second or two; there are plenty of macroscopic phenomena that you can’t understand without invoking quantum mechanics. Magnetism and the electronic behaviour of semiconductors are two everyday examples. And equally, many interesting nanoscale phenomena, notably virtually all of cell biology, don’t really involve quantum mechanical effects in any direct way.
So I’m going to stick to these twin definitions – it’s the nanoscale if it’s too small to resolve in an ordinary light microscope, and if it’s bigger than your typical small molecule.
Nanotechnology at the British Association
The annual British Association meeting is the main science popularisation event in the UK, and not surprisingly nanotechnology got a fair bit of attention this year. The physics section ran a session on the subject yesterday morning. First up was Nigel Mason, who organised the physics part of the meeting this year and thus could give himself the best slot. He’s an atomic and molecular physicist who does scanning probe microscopy; his talk was a standard account of nanotechnology from the point of view of someone who’s got a scanning tunneling microscope and knows how to use it; from Feynman via the IBM logo and quantum corrals to some of his own stuff about imaging DNA. Next was Mark Welland, who runs the Nanotechnology Centre at Cambridge University. Once he’d calmed down after the first talk, which had upset him in all sorts of ways, not least by talking about Drexler in what he thought was an insufficiently critical way, he talked about his group’s work on silicon carbide nanowires, which if they do nothing else have produce some of the prettiest images to come out of current nanoscience. Then it was my turn. As Mark Welland said, making his excuses for leaving early, “I know what you’re going to talk about because I’ve read your book“.
Harry Kroto, Nobel Laureate for his co-discovery (with Richard Smalley) of buckminster fullerene, was talking about nanotechnology in the chemistry section in the afternoon, but I didn’t get a chance to see it as I was roped into a rather tedious panel discussion about how the public perceives physicists. The final event for me was an appearance in a discussion event compered by the (excellent) BBC radio science journalist Quentin Cooper. This brought me the chance to share a platform with a poet, a paleontologist, and the government’s chief scientific advisor, Sir David King. We also got some free beer, though to Sir David’s horror this was bottles of (american) Budweiser rather than pints of bitter. So I got a final chance to make my nanotechnology pitch, though Quentin Cooper was rather more interested in trying to prise an unwise comment from the famously undiplomatic King. He happily confirmed that he still thought that global warming was a bigger threat than terrorism, he didn’t deny the suggestion that he’d received a rebuke from 10 Downing Street for saying this in the USA , where it’s language not thought suitable for a servant of the government of a loyal ally, and he was smilingly gnomic about who he wanted to win the US presidential election.
The BA is all about publicity, so it’s worth asking how much interest this attention to nanotechnology stirred up. For my part, I think my talk got a good reaction, I signed the first copy of my book for a stranger, I did an interview for Radio New Zealand, and got the approval and interest of one of the BBCs best science journalists. And I now know who’s reviewing my book for Nature (Mark Welland). But I don’t think the subject really caught fire. Maybe a rather febrile summer of nanotechnology coverage has left media people starting to be a tiny bit bored with the word.
Wiggly widgets in Small Times
A piece by Candace Stuart in Small Times gives a review of my book “Soft Machines”. I suppose that the publicist in search of a line for a book cover would choose the description of the book as “a rich and satisfying full-course meal” and the academic in me might approve of the line “This is not nano lite”, but I’m mostly pleased that the reviewer seems to have read the book and appreciated the main message.
A nearly nano-free week in California
I’ve been in Santa Barbara, CA, this week, finding out that traveling with two small children doesn’t leave much time for writing about nanotechnology or anything else. The occasion for the visit is the 65th birthday of Ed Kramer, a distinguished materials scientist at University of California Santa Barbara; it’s a part social, part scientific event bringing together his past and present graduate students, postdocs, and collaborators to celebrate his career so far and to thank him for his huge influence on our scientific careers (I was a postdoc with him between 1987 and 1989 at Cornell; these were two tremendously productive, educational and enjoyable years).
The scientific part of the proceedings consisted of a meeting with talks by his former students and collaborators. There were many nano-science luminaries around and much great stuff talked about; among those talking were Ned Thomas, director of the Institute of Soldier Nanotechnology at MIT, talking about photonic crystals, Herbert Hui with a beautifully lucid description of exactly why gecko feet are so sticky, Chris Ober from Cornell talking about new resist materials for making sub-30nm features, as well as rapid 3-d prototyping at the micron-scale using two-photon photo-polymerisation, and lots of other good stuff too.
Strangely, though, there was little mention of the nano word. Even the most distinguished of our number, faced with giving a talk in front of Ed, felt a bit like a graduate student again, in awe of the great man. Everyone has worked with him is in agreement that he’s someone who expects a lot from their students, who is quick to appreciate good work, and outstanding at standing back and making sure his collaborators get all the credit they deserve and more. But he’s got a low tolerance threshold for hype and fashion and we all knew that the way to get his approval is by telling a solid science story without any sweeping claims for grander significance.
I think we were all overcompensating. I asked Ned Thomas how he felt about now being very publicly labeled as a nanotechnologist, rather than as a polymer physicist. He thought there was a real difference; the science he did was rather similar, learning how to create nanostructures in polymers by self-assembly, but the focus had changed. It wasn’t so much that all his work now was focused on an immediate application, but the possibility of an eventual application provided a much more powerful steer on the direction of his work than was the case in the past. I think this rings true as a description of one of the changes in the sociology of science that nanotechnology as a concept has brought about.
Drexler responds
This morning brought a somewhat tetchy email from K. Eric Drexler, not entirely happy about my article in Physics World, The future of nanotechnology. There were three main complaints:
1. That he, Drexler, could not be held responsible for the “ridiculous artist’s concepts” that have become associated with his work. Thus my criticism of the nanosubmarine illustration isn’t a fair criticism of MNT. Actually, I have some sympathy with his predicament on this, in that I’m sure that the elementary errors that show up in the particularly silly image I chose wouldn’t be there if Drexler had had anything to do with it. Nonetheless, my criticism of these images does make one important point very clear – you shouldn’t expect macroscopic engineering design concepts to apply to directly to the nanoworld. Is this a fair criticism of MNT? I think it is – to quote from the preface of Nanosystems; “Molecular manufacturing applies the principles of mechanical engineering to chemistry”.
2. Next he argues that my statement that “Strong surface forces may make the moving parts of a NEMS device stick together and seize up” reflects a lack of study of the appropriate section of Nanosystems, chapter 10, which argues that very low friction is to be expected between atomically smooth diamond surfaces. It’s worth noting first of all that this statement in my article isn’t actually directed at MNT at all, but at top-down NEMS. Nonetheless, I do believe that the discussion in Nanosystems does substantially underestimate the problems of friction and dissipation at the nanoscale. This is a rather technical discussion, which I will enlarge on at a later time.
3. Finally, he objects that I have not proved my central contention, that biology is highly optimised for the nanoscale, pointing out that biology hasn’t been able to explore the space of non-aqueous molecular machine systems. This gets to the heart of the argument of Soft Machines. A crucial, though obvious, point, is that it only makes sense to talk about optimisation in the context of a particular environment, and what is optimised for ambient operation at 300 K in the presence of water is not the same as what is optimised for ultra-high vacuum at a temperature of 3 K. I wouldn’t exclude the possibility that MNT would work at 3 K in UHV, but I think that what works in ambient conditions is much more interesting, if only because medicine is likely to be such an important application of nanotechnology.